chevron_left
News
chevron_left
News
Examining the effects of wood interior building materials and wood fragrance on mental and psychotherapy
Psychotherapy Room of Wood", the scent of wood gives a boost to the introduction and continuation of treatment for depression.
Digital x Medical Open Innovation
July 5, 2024
July 5, 2024
To the press
Sumitomo Forestry Co.
BrainEnergy Inc.
The Jikei University School of Medicine
Examining the effects of wood interior building materials and wood fragrance on mental and psychotherapy
Psychotherapy Room of Wood", the scent of wood gives a boost to the introduction and continuation of treatment for depression.
Sumitomo Forestry Co. (President: Toshiro Mitsuyoshi; hereinafter "Sumitomo Forestry"), BrainEnergy Inc. (President: Mitsuhiro Kita; hereinafter "BrainEnergy"), and The Jikei University School of Medicine (President: Chiya Matsufuji; hereinafter "Jikei Medical University") have conducted research to clarify the effects of trees on depression and verified the effectiveness of the "Wood Psychotherapy Room". The research was conducted in a wood therapy environment. This study investigates whether a therapeutic environment using wood is effective as an adjunct to psychotherapy and psychotherapy for depressed patients.
Regarding fragrance, the "Tree Psychotherapy Room" confirmed that patients with higher levels of "depression and anxiety" were more likely to respond that fragrance is good for them. In the treatment of depression, how to introduce and continue appropriate treatment is an important factor. The results of this study suggest that a woody environment, especially the scent of wood, is effective in creating a positive impression and encouraging the introduction and continuation of treatment for depression. On the other hand, no difference in "room favorability" was observed between the "wood psychotherapy rooms" and the "regular psychotherapy rooms" with regard to anything other than fragrance.
The three parties have been conducting joint research on the "Effects of Therapeutic Environment Constructed with Wood Interior Building Materials and Wood Scent on the Effectiveness of Psychotherapy" since November 2020 (Reference: https://sfc.jp/information/news/2021/2021-07-19.html), and presented the research results at the 120th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Psychiatry and Neurology*1 in June 2024. The results of this research were presented at the 120th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Neuropsychiatric Society ※1 in June 2024.
■ Clinical Trial Summary
・The subjects were 20 patients with depressive disorders attending the Department of Neuropsychiatry, The Jikei University Hospital.
・The floor, walls, and desks of one of the two psychotherapy rooms of the same size in the same department were made of cedar wood.
・The patients were randomly assigned to one of two psychotherapy rooms of the same size in the same department, one of which had cedar wood floors, walls, and desks, and 10 patients each were given cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) ※2 by a licensed psychologist for 16 weeks.
・The study was conducted by using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale ※3 and Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) ※4 to examine the effects of different treatment environments on the effectiveness of psychotherapy and psychotherapy.
・The "desirability of the room" was measured in terms of (1) comfort, (2) aroma, (3) temperature, (4) space, and (5) brightness, each on a 7-point scale.
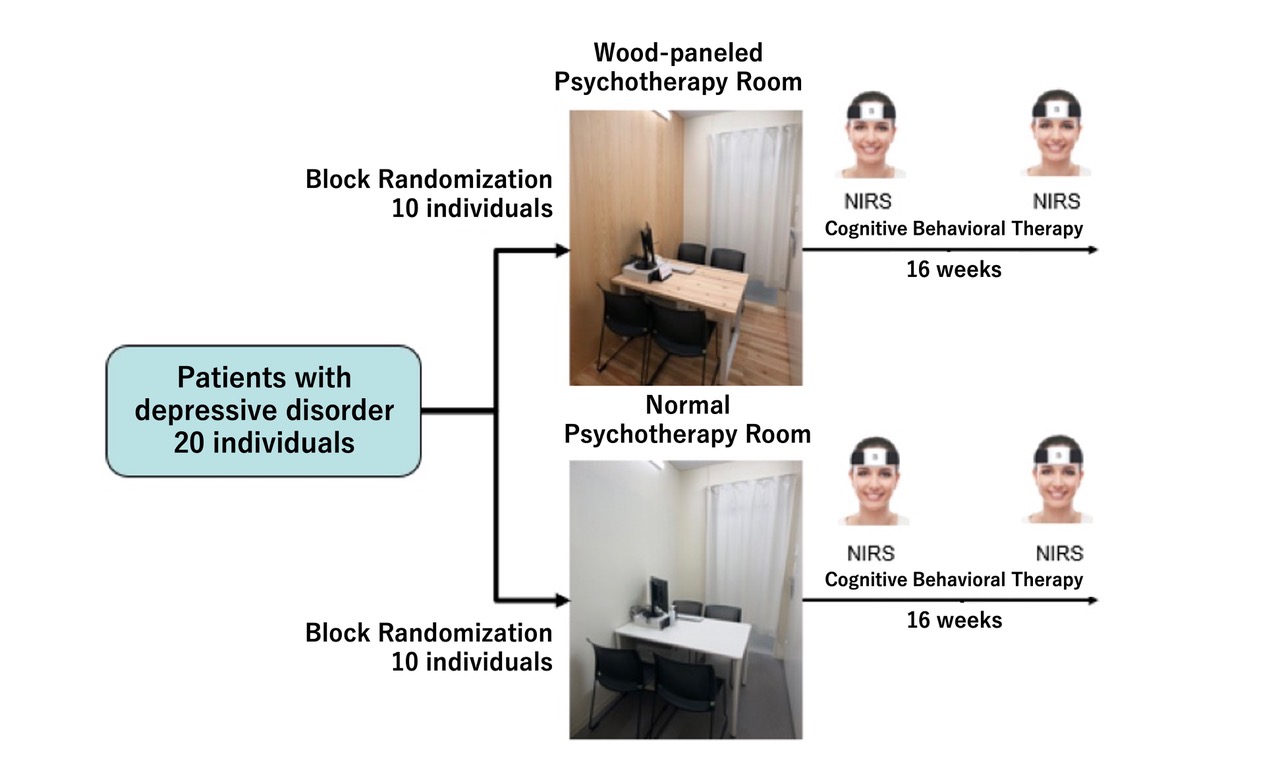
<Clinical Trial Flow>
■ Result
・In the NIRS, there were no statistically significant differences between psychotherapy rooms, but there were statistically significant differences between rooms in the "regular treatment room" and the "NIRS room" in the "room of psychotherapy" on a 7-point scale.
・Although NIRS showed no statistically significant difference between the different psychotherapy rooms, the measurement of room favorability showed a significantly higher score of 0.889 for the "wooden psychotherapy room" compared to 0 for the "regular treatment room" on a 7-point scale of fragrance favorability, leading to a favorable impression of the room. (Right figure).
・The likability of the fragrance tended to be higher the stronger the depression/anxiety, and the higher the percentage of respondents who answered that the fragrance was "good" ※6.
・The "room friendliness" was measured in terms of (1) comfort, (2) fragrance, (3) temperature, (4) space, and (5) brightness, but no differences were observed in any of the categories other than (2) fragrance.
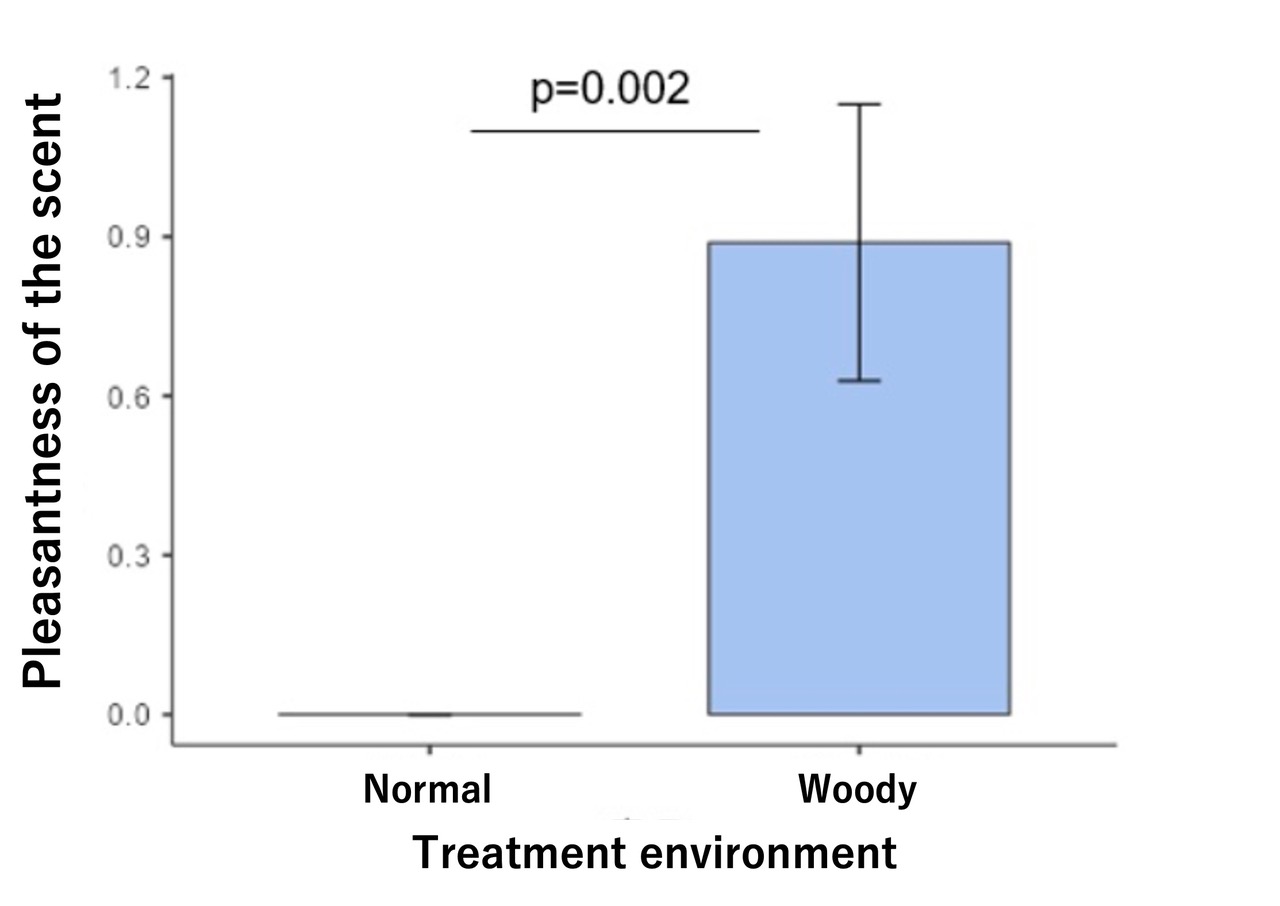
<Indoor desirability measurement and fragrance>
In recent years, mental disorders have been on the increase worldwide, with depression being one of the major social problems. Although pharmacotherapy such as antidepressants can be very effective when used appropriately, pharmacotherapy is not always proven to be effective for so-called "mild depression. In addition, psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavioral therapy is effective in the recovery phase of depression, and the importance of alternative or adjunctive therapies other than drugs is recognized. Natural elements such as plants and wood are expected to reduce depression and anxiety, and "biophilic design ※5" is attracting attention as a method to support stress improvement.
We will make use of the results of this joint research for further exploration, and aim to provide better services and create more comfortable spaces for a wider range of people.
※1 The Japanese Society of Neuropsychiatry is one of the largest neuropsychiatric societies in Japan with over 20,000 members.
The 120th Annual Meeting will be held at the Sapporo Convention Center/Sapporo Industrial Promotion Center on June 20-22, 2024. The annual meeting is attended by more than 7,000 members each year, and the program provides a panoramic view of progress in a wide range of fields of psychiatry.
※2 Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A therapy that works on the way one perceives and thinks to create a state of mind that can better cope with stress and enhance adaptability.
※3 Hamilton Depression Rating Scale: A scale to evaluate the severity of depression published by Hamilton in 1960. A psychological test in which doctors and other specialists evaluate each item characteristic of depressive symptoms. It evaluates 17 items including "depressed mood," "guilt," and "difficulty falling asleep.
※4 Near-infrared spectroscopy: A technique that uses near-infrared light to measure changes in the oxygenation state of hemoglobin in the brain and indirectly measure brain function based on changes in blood volume in the brain.
※5 Biophilic design: A technique that incorporates biophilia, the concept that "(humans) have an innate desire to connect with nature," into spatial design.
※6 Positively correlated with the "Depression" item of the Mood Profile Test (POMS) (p = 0.47)
<Background, Collaborative Research Structure>
(1) Sumitomo Forestry Co.
The Tsukuba Research Institute was established in 1991 as a center for research and development aimed at the comprehensive use of wood.The Tsukuba Research Institute has scientifically verified the functions and characteristics of wood and greenery, and their effects on the human mind and body, and utilized them in the creation of comfortable spaces. In this joint research, he was mainly in charge of creating the research plan and supervising the construction of wooden interior building materials, wood fragrances, and other environmental features.

(2) BrainEnergy Inc.
BrainEnergy has been analyzing vast amounts of central nervous system data with medical institutions and research facilities in Japan and abroad, and is working to develop technologies to support brain activity and body function and to construct spaces using biophilic design and digital medical technology. In this joint research, he is primarily responsible for the development of the research plan, supervision and construction of the treatment environment, and data measurement and analysis evaluation.
(3) The Jikei University School of Medicine
A private medical school founded in 1881. The university practices patient-centered medicine in accordance with its founding spirit, "Don't diagnose the sick, diagnose the sick.The university is committed to fostering good medical professionals through medical treatment, education, and research. The university has four affiliated hospitals, including the affiliated Kashiwa Hospital (Kashiwa City, Chiba Prefecture), centered on the affiliated hospital (Nishi-Shinbashi, Minato-ku, Tokyo), and aims to be a university and affiliated hospital that leads medical care, education, and research, from community medicine to advanced medical care, and from basic research to clinical research, utilizing its collaborative capabilities with local medical institutions. In this joint research, the University's Department of Psychiatry is primarily responsible for the preparation of the research plan and evaluation of the medical aspects of the research.
Thank you.
≪Contact information regarding releases≫
Mr. Sato, Corporate Communications Department, Sumitomo Forestry Co.
TEL:03-3214-2270
DxMedical Division, BrainEnergy Inc.
email:info@brainenergy.jp
Public Relations Division, Corporate Planning Department, Jikei University Educational Corporation



